 The light that enters your eye allowing you to see has come either directly
from a source, like a light globe, or has come from a source, been reflected
off an object, and then to your eye. Look around you, most things you
can see are due to reflected light from an object to your eyes. Your eyes
then transmit this information to your brain via the optic nerve which
then interprets the electrical signal as light of a particular colour and
intensity. You can see an object only because it either reflects light
from a surface, or because the object itself emits light.
The light that enters your eye allowing you to see has come either directly
from a source, like a light globe, or has come from a source, been reflected
off an object, and then to your eye. Look around you, most things you
can see are due to reflected light from an object to your eyes. Your eyes
then transmit this information to your brain via the optic nerve which
then interprets the electrical signal as light of a particular colour and
intensity. You can see an object only because it either reflects light
from a surface, or because the object itself emits light.
![]() Some surfaces, like gloss paint, are shiny, and reflect a fairly good
image back to your eye. Others, like matt paint or paper do not reflect
a clear image. They all reflect light but the reflected light is spread
unevenly and is called a diffuse reflection.
Some surfaces, like gloss paint, are shiny, and reflect a fairly good
image back to your eye. Others, like matt paint or paper do not reflect
a clear image. They all reflect light but the reflected light is spread
unevenly and is called a diffuse reflection.
For an almost perfect reflection glass coated with a thin layer of metal on the back is used. This is called a mirror and a totally flat mirror is called a plane mirror.
Plane mirror reflection
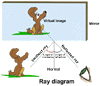 From
the diagram you can see that the ray of light travelling towards the mirror
is the incident ray and the ray leaving the surface is the reflected ray.
A line drawn at right angles to the mirror is called the normal. There
are two basic laws of reflection for light from a plane mirror. These
laws are not new, in fact they were recognised by Plato around 400 BC.
From
the diagram you can see that the ray of light travelling towards the mirror
is the incident ray and the ray leaving the surface is the reflected ray.
A line drawn at right angles to the mirror is called the normal. There
are two basic laws of reflection for light from a plane mirror. These
laws are not new, in fact they were recognised by Plato around 400 BC.
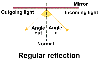
They are:
- The reflected ray, the incident ray and the normal at the point of
incidence are all in the same plane.
- The angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence.
These laws apply to all the rays of light reflecting from the mirror.
Mirror images
 When you look at yourself in a plane mirror you see a reflection or an
image of the same size, that moves closer and further away to "mirror"
what you do. You should notice two other effects that are important. Firstly,
the image appears to travel towards you or away from you at twice your
speed. Secondly, if you raise your left hand, the reflected image raises
its right hand.
When you look at yourself in a plane mirror you see a reflection or an
image of the same size, that moves closer and further away to "mirror"
what you do. You should notice two other effects that are important. Firstly,
the image appears to travel towards you or away from you at twice your
speed. Secondly, if you raise your left hand, the reflected image raises
its right hand.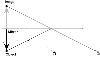
From this simple ray diagram you can see that the image is as far behind
the mirror as the object is in front, and reversed.
Real or virtual?
The image in a plane mirror appears to be behind the mirror, if you were
to look behind the mirror you would see nothing. This type of image is
called a virtual image. Virtual images are only formed by mirrors. The
other type of image is one that can form on a screen, like in a slide
show. These images are called real images. A real image can be shown on
a screen, a virtual image cannot be shown on a screen.
A piece of paper does not reflect light to produce image but the same laws of reflection apply. Why doesn't the paper reflect light in a way that produces a clear image if these laws of reflection apply? Because the surface of the paper is uneven, light reflects from each section but as the reflected rays emerge in many different directions, it appears scattered. This is called diffuse reflection. Gloss paper does produce a better image because the coating on the surface fills some of the irregularities, so reducing scatter.
| Copyright owned by the State of Victoria (Department of Education and Early Childhood Development). Used with Permission. |