| Earth and
Beyond |
|
| The changing Earth |
The Earth
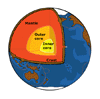
The Earth is covered with a hard
crust that varies from 5 to 64 kilometres thick. No one has ever dug below
the crust, but scientists have an idea of what the Earth is like on the
inside of the crust. Under the crust is a layer of soft rock called the
mantle. At the top of the mantle the rock is very hot and liquid. It is
moving around all of the time. Deeper in, the crust the rock is more plastic
and nearly solid. Within the mantle is the core of the Earth
The centre of the Earth is called
the core. The outer core is made of hot liquid metals, mostly iron and
nickel. The inner core is solid iron and nickel metal. The temperature
in the centre at the Earth is thought to be as high as 4000°C.
It is about 6300 kilometres to
the centre of the Earth. The Earth is surrounded by an atmosphere, 1000
kilometres wide. The atmosphere is composed of a mixture of gases including
nitrogen, oxygen, water vapour, argon and carbon dioxide.
Weathering
 Weathering
is the process of breaking down rock into smaller particles. Wind, changing
temperatures, water, ice, acidic rain and plants can break down surface
rock to form soil.
Erosion

Weathering causes erosion. Cutting down
trees and burrowing animals such as rabbits can also loosen the soil and
cause erosion. After the rock and soil structure has been changed and
dying roots no longer hold the particles together erosion takes place.
The wind can blow the particles away or water washes them into streams,
rivers and oceans. Planting trees and ground cover can reduce the effects
of erosion.
Salinity

Salinity
is a major problem in country Australia. With too much irrigation or clearing
of trees and bush, the surface soil can become salty and infertile as
a result of rises in the underground water table. The water table is
the level of water naturally stored underground. As the water table
rises
it brings with it dissolved salts from deep in the soil. These salts
then kill surface vegetation, which further magnifies the problems of
the farmer.
When this salt gets into the rivers, their water becomes unusable for
drinking or irrigation.
Links:
 The structure of the Earth
The structure of the Earth
 Earth Earth
 Erosion Erosion
 Weathering
Weathering
 Deposition Deposition
|
![]()


![]() The structure of the Earth
The structure of the Earth
![]() Earth
Earth
![]() Erosion
Erosion
![]() Weathering
Weathering
![]() Deposition
Deposition