Other symbols
from electronics
In electronics, miniature components are often
used. In this section you will learn their symbols,
and what each component does.
Transistors
 Transistors
are tiny semiconductor devices that are used to
switch or amplify currents and voltages. There are
many different types designed to perform specialised
tasks. Transistors allowed radios to be made portable
as they replaced cumbersome valves. Portable radios
are sometimes called "transistors" or
"trannies". The transistor was invented
in 1947, and the three inventors, William Shockley,
John Bardeen and Walter Brattain, won the Nobel
Prize for Physics in 1956.
Transistors
are tiny semiconductor devices that are used to
switch or amplify currents and voltages. There are
many different types designed to perform specialised
tasks. Transistors allowed radios to be made portable
as they replaced cumbersome valves. Portable radios
are sometimes called "transistors" or
"trannies". The transistor was invented
in 1947, and the three inventors, William Shockley,
John Bardeen and Walter Brattain, won the Nobel
Prize for Physics in 1956.
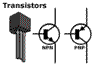 Transistors
can operate as switches or amplifiers, making them
very useful components in electronics. Transistors
are polarised and must be connected the right way
round. Two types are NPN (negative - positive -
negative) and PNP (positive - negative - positive).
Transistors
can operate as switches or amplifiers, making them
very useful components in electronics. Transistors
are polarised and must be connected the right way
round. Two types are NPN (negative - positive -
negative) and PNP (positive - negative - positive).
Integrated circuits
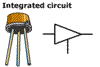 Integrated circuits (ICs) can have many components
for a radio on a tiny silicon "chip",
which enables electronic equipment to be extremely
small. An example is the identification chip that
can be placed under your pet's skin in case it gets
lost. Simple ICs have three pins, ICs in your computer
have many more pins. Modern computers and other
devices can have hundreds of intergrated circuits
combined into one chip. A CPU (Central Processor
Unit) is an IC that can perform hundreds of tasks
per second or faster and may contain 20 million
or more transistors.
Integrated circuits (ICs) can have many components
for a radio on a tiny silicon "chip",
which enables electronic equipment to be extremely
small. An example is the identification chip that
can be placed under your pet's skin in case it gets
lost. Simple ICs have three pins, ICs in your computer
have many more pins. Modern computers and other
devices can have hundreds of intergrated circuits
combined into one chip. A CPU (Central Processor
Unit) is an IC that can perform hundreds of tasks
per second or faster and may contain 20 million
or more transistors.
Capacitors
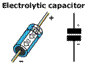 |
Basically, capacitors
store electrical energy, then release it in
one hit. This is the symbol for a polarised
capacitor: Note how this differs from the symbol
for a cell - both lines are the same length. |
 |
|
The unit for capacitance is
the Farad, named after the Englishman, Michael
Faraday. In the circuits you are likely to
use, capacitance is measured in microfarads
(µF), or a unit one thousand times smaller,
the picofarad (pF).
|
Light emitting
diodes
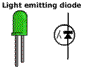
| In miniature circuits,
light globes are too big. The small coloured
light on your stereo, computer or video camera
is a light emitting diode (or LED). Light emitting
diodes are used in the flashing red lights that
cyclists have on their bikes. They don't use
much power and, by using capacitors in the electronic
circuitry, the lights flash as well. |
 |