|
Electrical symbols
It can be difficult to draw electrical circuits, so to make it easier
a system has been devised with symbols for each of the electrical components.
In this topic you will be introduced to some of the more important components
of electrical circuits and their symbols. See the topic Electric
circuits for more on the operation of simple circuits.
Some of the basic
symbols
The basic parts of a circuit are a power source or battery, wires, and
a resistance or globe. Switches are also incorporated into circuits
to control the flow of electric current.
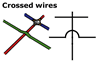
The connecting wires in a circuit are represented by straight lines
with dots to show where they are joined. If one connecting wire passes
over another, without electrical contact, the symbol looks like a small
bridge.
The symbol for a cell has two parallel lines at right angles to the
connecting wires. The thinner line marks the positive terminal of the
cell and the thicker, shorter, line marks the negative terminal.

A battery (more than one cell) is drawn as a series of cells, each usually
adding 1.5 volts. A 6 volt battery looks like:
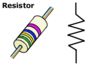
Resistors are devices that transform electrical energy supplied by the
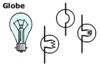
battery into thermal energy. Electric globes are resistors, changing
the electrical energy into thermal energy and light energy.
The symbol for a resistor is:
|
The symbol for a globe is:
|
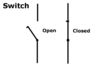
Switches are used when it is required to turn a circuit on and off.
Switches have two states: open (off) and closed (on).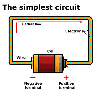
Look at this simple circuit and their diagrams. Identify each of the
components in the pictures and from the symbols.
Cells in series and parallel
Combinations of cells or batteries are discussed in the topic Batteries
in series and parallel. Here we look at how their arrangements are
represented.

Cells in series are drawn as individual cells in a line, usually shown
head to tail with no connecting wires.
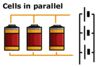
Cells in parallel are drawn as cells sitting besides each other, with
connecting wires.
|