When solids or liquids dissolve in a liquid solvent they form a liquid solution. Liquid solutions cannot be separated by sedimentation or filtration as the particles are too small to catch in a filter and too light to settle out.
Recrystallisation and distillation will separate the components in a solution using the difference in boiling points of the components. This topic investigates some simple examples of separation by recrystallisation and distillation.
Recrystallisation
 Recrystallisation
occurs when the liquid solvent particles in a solution are boiled away,
or evaporated off, from a solution of a solid in a liquid solvent. The
dissolved solid will eventually form crystals in the container as the
solvent particles leave the solution.
Recrystallisation
occurs when the liquid solvent particles in a solution are boiled away,
or evaporated off, from a solution of a solid in a liquid solvent. The
dissolved solid will eventually form crystals in the container as the
solvent particles leave the solution.
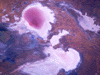 The
salt pan in Lake Eyre, for instance, is laid down by recrystallisation
occurring naturally as water from the feeder rivers evaporates off in
the Sun light. Industrially, recrystallisation is also used to obtain
salt from seawater.
The
salt pan in Lake Eyre, for instance, is laid down by recrystallisation
occurring naturally as water from the feeder rivers evaporates off in
the Sun light. Industrially, recrystallisation is also used to obtain
salt from seawater.
Distillation
 Distillation is used to separate a solution of two or more dissolved liquids
or to collect the solvent from a solution of a liquid and solid. In recrystallisation,
the liquid solvent is usually lost to the atmosphere, but in distillation
the liquid being boiled off is cooled and collected. No part of the solution
is lost.
Distillation is used to separate a solution of two or more dissolved liquids
or to collect the solvent from a solution of a liquid and solid. In recrystallisation,
the liquid solvent is usually lost to the atmosphere, but in distillation
the liquid being boiled off is cooled and collected. No part of the solution
is lost.
Distillation separates the components of a liquid solution according
to their boiling points.
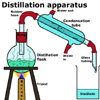
To set up a distillation:
- the solution is poured into the distillation flask.
- the condenser is attached and connected to the water supply.
- the collection flask is placed under the outlet of the condenser.
- a heat source is placed under the distillation flask.
- a thermometer can be placed in the top of the distillation flask to record the temperature of the vapours coming off the solution.
As the solution is heated the component of the solution with the lowest boiling point will start to boil first. The rising vapours pass into the condenser and are cooled by the water in the water jacket around the condenser. The vapours then condense back into a liquid and are collected in the collection flask.
When all of the first component has boiled off, the temperature will rise until the next liquid component starts to boil. The second component can then be collected in the same way as the first. This process can keep on occurring until all of the different liquids in the solution are separated. In the case of a solid in a liquid solution, the liquid will boil off leaving the solid in the distillation flask.
| Copyright owned by the State of Victoria (Department of Education and Early Childhood Development). Used with Permission. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||